

VCE Applied Computing Notes by Mark Kelly
Software DevelopmentVCAA Exam Post Mortem2009
|
Post Mortem Notes This is not a VCAA publication.
I do not speak for the VCAA, the IT examiners, or exam markers. I was not involved in the writing or marking of this examination. Extracts from exams are all Copyright © VCAA, and are used with permission. Use these post mortems at your own risk. I reserve the right to change my mind completely, at short notice, about anything I've said here. Suggestions, discussions and corrections are welcome. Questions look like this. |
|
Other VCE IT Exam Post Mortems to enjoy IPM / ITA / Informatics / Data Analytics - 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2023
|
|
Examiners' comments were published: 14 April 2010 Sept 2012 - For those using old exams for revision purposes, I've marked questions that are no longer relevant in the 2011-2014 study design. The notes appear after the question numbers. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This year I am introducing a new award: the Happy Dog award, for when I'm happy with the examiners.
I'd do the same for the ITA exam, but I'm afraid they're never likely to earn one. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Written examinationThursday 12 November 2009 Reading time: 3.00 pm to 3.15 pm (15 minutes) Writing time: 3:15 pm to 5:15 pm (2 hours)
• Students are permitted to bring into the examination room: pens, pencils, highlighters, erasers, sharpeners, rulers and one scientific calculator. Materials supplied • Question and answer book of 22 pages with a detachable insert containing a case study for Section C in the centrefold. Instructions • Remove the insert containing the case study during reading time. At the end of the examination • Place the answer sheet for multiple-choice questions inside the front cover of this book. Students are NOT permitted to bring mobile phones and/or any other unauthorised electronic devices into the examination room. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2009 Assessment Report, the examiners said of the exam: (the emphasis is mine) During the examination, students should: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SECTION A - Multiple-choice questionsInstructions for Section A Answer all questions in pencil on the answer sheet provided for multiple-choice questions.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 1 (2011-2014 - while topologies may still be relevant to the study design, bus topology is now largely extinct) A major weakness of a bus topology is A. if there is a cable break the whole network is likely to fail Answer is A. Bus topology is wired like a string of Christmas tree lights: a single blown bulb stops the entire string of lights. Also, bus topology requires coaxial cable: try finding a NIC with a BNC (bayonet) port nowadays! 77% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 2 When writing an algorithm, logic errors can occur. A. check the variable names. Answer is C. It's deskchecking. Running a program will certainly highlight syntax errors. 78% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 3 (2011-2014 - SDLC is now PSM, and testing is no longer a separate step) The writing of a computer program's code for a new system occurs in which phase of the Systems Development Life Cycle? A. development phase Answer is A. Has to be development. 80% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Question 4
A random access file is best described as a file where records A. have no fixed length. Answer is D. Random files are made of records of fixed length (unlike sequential files). Because their lengths are known, the location of a record can easily be determined by position = (recordnumber-1) * recordlength + 1 58% of the state got this right. 19% went for A and 18% chose C. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 5 The best reason for using a naming convention for program elements is that A. it makes the program run faster. Answer is D. The other options are silly. Names disappear during compilation; naming does not affect ease of use; and users don't need to read the source code. 88% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 6 (2011-2014 - SDLC is now PSM, and implementation is now part of the development stage. The answer now would be 'development') A disaster recovery plan documentation would be prepared in which phase of the Systems Development Life Cycle? A. design phase Answer is D. Documentation occurs during implementation (unless you're using an SDLC with a separate documentation phase.) Documentation can't be written until the product is finished (so rule out options A and B) and evaluation occurs way after implementation. 27% of the state got this right. 47% chose A. It appears that many students considered the preparation of a disaster recovery plan in the same way as the development of evaluation criteria, which takes place in the design phase. The study design explicitly lists disaster recovery plans as part of the implementation phase. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 7 (2011-2014 - only basic project management is now required. Critical paths are not needed.) Project management requires precise scheduling of time throughout the duration of a project. Within this schedule there will be a set of tasks that must be completed on time if the project is to finish on time. A. goal. Answer is D. The critical path is the series of tasks from the start to the end of a project that must run on time if the project is to finish on time. In other words, they have no slack. 71% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 8 (2011-2014 - implementation is no longer relevant) A company has decided to introduce a new system into three stores initially, and then three additional stores each fortnight until all stores are online. A. parallel. Answer is B. It sounded a bit like 'pilot' when it said 'three stores initially' but those stores were not used to test the system and learn lessons from so the full rollout would be more successful. Bringing change in in stages is phased implementation. This is not how I usually use the term 'phased'. I see it as bringing in a single system a piece at a time. e.g. all the computers get stage 1 done, then all of them get stage 2 done, etc. 78% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 9 User documentation that details the steps to take in order to operate software is called A. a Quick Start Guide. Answer is C. It's not the others: quick start guides just help you get over the first hurdles using the product; installation guides help you get it into the system and set it up for first operation; technical reference is for extending, modifying, repairing the product. I've not often heard of a Procedures Manual used in this context. Usually procedures manuals relate to human/office procedures. In IT, it's more often called a user manual. 61% of the state got this right. 29% went for A. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 10 Using encryption software when transmitting data means A. data intercepted on route is unreadable. Answer is A. A pretty simple question. Encryption renders information unreadable to unauthorised people. It does not prevent interception, nor make transmissing faster. Packet size is irrelevant. 87% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 11 Mary works at a digital photo processing shop. The staff save the files brought in by customers onto the hard disk of a desktop computer before processing them. At the end of each day Mary copies all the photo files that have been processed onto DVDs. She places the DVDs into a fireproof cabinet and deletes all the copied files from the desktop computer's hard disk. A. backing up of files. Answer is B. Backing up makes a copy of the original, and does not delete the original. Archiving puts the original into offline storage (not immediately accessible without first mounting the storage medium) and deletes the original; disposal is pure deletion with no copies left. Encryption is irrelevant. 75% of the state got this right. 19% chose A. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following information relates to Questions 12-16. A program is being purpose-designed for the Australian Underwater Surf Association. It will be used to manage a very large amount of data about the association's members.
The software developer trialled the user interface with users for two weeks. At the end of the two weeks, users reported their experience to the developer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 12 During the trial period users had to edit the details of several hundred members. The information about changes to member details came mostly by email, some examples of which are shown.
Which single feature of the user interface would cause the most annoyance to users? A. the placement of the buttons Answer is C. Obviously. There's nothing particularly hideous about the button placement; B&W would not add nor detract much from usability; the font changes may be irritating but are otherwise trivial. The sorting of users by membership number makes sense to a database, but is useless as far as a human is concerned. 58% of the state got this right. 17% said A and 22% said D. 2023 addition: VCAA should have added option E: So sloppy, VCAA. How many people checked, edited, approved, printed and distributed this exam before it was given to annoy literate students? |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 13 When the 'save' button is clicked the program can take up to one minute to save all the data. The trial users reported that they did not know how long they might have to wait or when they could start editing again. A. program in a 'meter' which displays how much is left to save and disappears when the save is complete. Answer is A. Animated progress meters are important for humans who tend to get nervous when computers seem to have possibly frozen: they tend to anxiously push all sorts of buttons as their panic increases. A reassuring message indicating an ETA at least tells them that things are well. It is better than a static "please wait" which could indeed cover up a software freeze. Telling the person after the event does nothing to help them during the event! D may make sense to the programmer who knows what is 'normal' waiting time, but it does not help a casual user. 78% of the state got this right. No one chose D. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 14 From the screen shot of the user interface, what evidence is there of a serious error in the data validation process? A. A help button is missing. Answer is C. While spelling errors may be included in 'validation', it's cosmetic and is not serious. Validation can also check for text case (upper,lower,title etc) but again it's not serious. Invalid data such as an meaningless value, however, can cause serious processing errors or inaccurate information. 88% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 15 When the program is running it stores the data shown in the screen shot in an array of records called NAMES. Another array of records called CONTACTS is used to store contact details for each member. When the program's user clicks 'edit' that member's contact details are displayed on the screen. The field most likely used by the program to link the two arrays is A. Member ID. Answer is A. It's a unique identifier (like a key field in a database) that cannot possibly occur more than one by chance. People's names and genders can obviously be duplicated.
But key fields and relational databases are in the ITA course, not SD... Bad examiners are going beyond the study design! Sorry guys - you're not allowed to do that.
84% of the state got this right. Nearly everyone else chose B. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 16 Member ID numbers must be between 1 and fifty thousand (50 000). When a new member is added, the program uses the following code to generate a new member ID number. Member ID = 1 + int(rand( )* 100000/2)
int( ) returns the integer part of whatever number is in the brackets. If a new member is being added and rand( ) returns 0.002222 then Member ID will be set to A. 2 Answer is C. The deskcheck is as follows: > .002222 * 100,000 = 222.2 (remember your order of operations! * and / have the same priority so work them from left to right) It's damned good to see the examiners using some realistic functions in their pseudocode.
I've previously grumbled about restricting pseudocode to the complexity of a four-function calculator. As long as the behaviour of the pseudocode functions is made clear, bring 'em on! And the question was challenging, but not too hard for the average student. 2023 note: it's a shame the logic of the entire algorithm is rubbish. Generating a random ID number totally ignores the very real fact that the number may already be in use. D'oh! 59% of the state got this right. 19% chose D and the rest were evenly divided between A and B.. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The following information relates to Questions 17 and 18. ASM is a small business that has a suite of offices on the first floor of a building. It uses an old local area network (LAN) for its business operations. A floor plan of two offices and part of the LAN are shown in the following diagram.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 17 When the LAN was first installed its goal was to improve the overall efficiency of the transfer of information within the business. A. to eliminate the need to copy data to and from CD. Answer is A. Has to be, because the other options can be ruled out. Keep in mind the key words of the question's stem. They want to improve the efficiency of information transfer. Can't be B - Improving clarity of info is not an efficiency measure: it's effectiveness (quality of the product, how well it achieves its goals) 60% of the state got this right. 28% chose C. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 18 (2011-2014 - It's doubtful whether detailed questions on topologies are still relevant) ASM's local area network is now outdated and it no longer meets its system goal. It has been suggested that a new network be installed as shown in the following diagram.
Based on the two network diagrams, the topology of the network is most likely being changed from A. a star network to a bus network. Answer is D. The original LAN had cables from the workstation all connecting (via T-pieces) to a single (coaxial) cable that led to the server. That's 'bus' and is now superseded. The new LAN has individual (CAT5e or CAT6) UTP cables from workstations going to a switch which has a single cable leading to the server. That's star topology, and it the norm for SOHO (Small Office / Home Office) LANs. 77% of the state got this right. Most who got it wrong chose C. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 19 (2011-2014 - skip this. NSDs are no longer relevant)
The output for the Nassi-Shneiderman diagram above would be A. 2 Answer is C. Get a scrap piece of paper and do a walkthrough: A=1 52% of the state got this right. 17% chose A, 22% chose B and 10% chose D. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 20 A software company has a policy that 50% of all lines in a program must be internal documentation lines. The reason for this is A. it makes the program easier to use. Answer is D. Internal documentation is ignored during compilation and is never seen by the program's user. It doesn't improve the performance of the code it's in. It doesn't affect the readability of the code. It does help later programmers understand why things were done as they were so they can maintain the code after the original programmers are long gone with all their understanding of the code. 86% of the state got this right. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SECTION B - Short answer questionsInstructions for Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 1 (2011-2014 - time/date data types are no longer relevant, and character has been added) A clothing store Data Base Management System (DBMS) is being updated to include more fields about items on sale. The following field types are available.
4 marks - state average was 3.2 Colour and date purchased are clear enough. I like the way the examiners provided a sample phone number to make it clear why number was not acceptable - a number cannot store parentheses, spaces or leading zeroes! And I like the way the examiners expect SD students know Boolean by name and did not append "true/false" to it.
Students were provided with a list of possible field types and were asked to select the most appropriate field type for each of the fields listed in the table. This question should have been highly accessible to students but it was disappointing that only 40 per cent of students were able to provide all four responses completely and appropriately. Many students responded incorrectly for 'Supplier' with numeric; however, the example clearly indicated that brackets and spaces would be entered so a numeric data type would not be able to contain these characters. Many students also could not identify the Boolean data type. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 2 (2011-2014 - skip this. Global data stuff is no longer relevant) Robert owns a small business selling handmade model cars. Recently there has been more interest from overseas customers. He has decided to launch a website to take orders for the sale of his model cars online.
3 marks - state average 2.2 On the printed exam, each advantage had 3 lines of space for answers - rather a lot for 'listing' things! I'm concerned the amount of space provided might encourage students to describe or explain rather than just list. Appropriate responses included: A variety of potential advantages were provided; however, a number of students selected one advantage, such as 'increased customer base', and wrote it in three different ways. Students needed to provide responses that related to the business scenario described. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 3 A school has decided to purchase a new electronic roll-marking software package. The software allows teachers to mark a student absent by scanning a barcode printed next to the absent student's name in the rollbook. This is done by using either a portable computing device that has a built-in barcode reader or by using a barcode reader that can be attached to an existing portable device. The information is then transmitted wirelessly to a central computer which alerts the coordinators of students absent from class. As the school supplied its staff with portable computing devices just last year, the principal wants to purchase only barcode readers which staff can use on their existing devices. Before purchasing the new system the school needs to check the specifications of the existing devices. From the list below select the three features that the existing portable computing devices must have for the roll-marking system to work and justify your selection. A large 8.2" screen 6 marks - state average 5.1
Why not the others? A large 8.2" screen - a large screen may be easier to read, but is not a "must have" (B) Ability to store and run additional software ---
The roll-marking program that is to be used does not come as part of the Given the school scenario provided, the three features listed in the table above were the essential features. Students may |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 4 A program is needed to process data for stock items. The data is stored in a file on disk. The file could contain up to 500 records. Three typical records are shown in the following table.
Juan, a novice programmer, is writing the program. He has chosen a programming language that recognises the following data types: integer, floating-point decimal, text and Boolean. It will also allow the creation of data structures such as arrays and records. a. Explain why this is not the most appropriate choice of data type. Integer can't store the decimal fraction (cents) of the cost. The following is an example of a good student response. 2 marks - state average 1.1 b. State the data type he should have chosen. Floating point. 1 mark - state average 0.7 Hmmm. Another data type question? We just had that in question B1 above. Juan knows that for the program to run most efficiently it should read all the relevant data into memory first. He starts by making a large number of variables: ItemCostl, ItemCost2, ItemCost3, and so on. A colleague sees this and tells Juan that an array will be much more efficient. Explain why. [7 lines provided] Values stored in arrays can be addressed by their index number, which allows the use of loops to traverse or address any number of values rather than by addressing discrete variables by name. Juan is an idiot. Which company was dumb enough to let him loose on their data? 2 marks - state average 0.8 Students should be able to describe data structures, the advantages of their use and their weaknesses. Many students did not provide a response to the question, which is disappointing as data structures feature in both Units 3 and 4. The following are examples of acceptable student responses. - An array only has to be defined once and can hold a large amount of items in its list. The array can be easily loaded up at the start of the application, more quickly then loading up large amounts of variables, therefore saving on time thus being more efficient. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 5 A programmer wishes to check that when a new product number is entered, it is valid and within the prescribed limits. If it is invalid then the user needs to know why. The programmer has chosen to validate the data in the following order: Existence test, Numeric test, Range test. Explain why this order is necessary. The validation tests are dependent on preceding tests. Later tests are pointless if a preceding test has already failed. If the data does not exist, no following test makes sense; if it's not numeric, a range test is pointless. 3 marks - state average 1.8 In general, students made a reasonable attempt at responding to this question. It was clear they knew the reason for the validation order; however, many had difficulty explaining why the order was necessary without simply restating the question. Students need to practise questions that require them to articulate programming concepts, not simply utilise these concepts while programming. The following is an example of a good student response. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
END OF SECTION B - Total 21 marks
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CASE STUDY INSERT FOR SECTION C
Truss-Tee organisation
Figure 1 The business is almost 30 years old and has factories in Melbourne, Sydney, Brisbane and Perth. Current system - hardware and software The hardware specifications for one factory are shown in the network diagram (see Figure 2).
RoboCut is a computer-controlled timber cutting system.
Current system - people and their roles Each factory has a manager, two designers and eight assemblers.
The data flow and processing described above is shown in the data flow diagram (DFD) below. 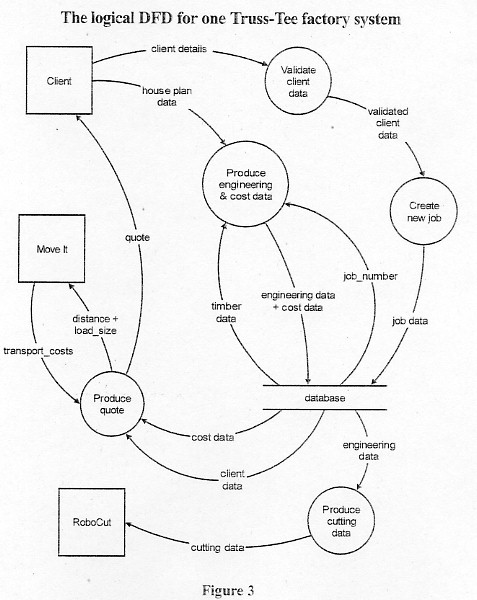
Last year two designers resigned from Truss-Tee, one from the Sydney factory and one from Melbourne. With an Australia-wide skill shortage, Truss-Tee has not been able to find two qualified carpenters who can do the designer jobs. It has tried to retrain some of the assemblers, but this has not proved successful. Later this year the other designer in Melbourne is due to retire. Truss-Tee is very concerned about how it can continue to provide high quality service if it cannot obtain skilled carpenters. Shaun Truscott is the managing director of Truss-Tee. He is aware that each factory has times when its designers have little to do. If their workload could be shared across the four factories, Truss-Tee would not need so many designers. END OF CASE STUDY INSERT FOR SECTION C
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Instructions for Section CAnswer all questions in the spaces provided. Remove the case study insert and read all the information provided before you answer these questions. Answers must apply to the case study. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 1 (2011-2014 - reasons for change are no longer relevant) To help understand the existing system, Rose first tries to identify the main reason for Truss-Tee wanting to change its system. a. State the main reason for Truss-Tee changing its system. Qualified designing staff are hard to find, yet they spend considerable time doing nothing. This results in both a shortage of skills and a waste of wages. 1 mark - average 0.5 b. Is this a technical, economic or social factor? Economic. 1 mark - average 0.5 It was disappointing that less than 50 per cent of students were able to identity the reason for change (Question 1a.) or that it was a social factor (1b.). This type of question has been done poorly by students for a number of years. Teachers should model questions regarding factors promoting change on Question 1 (Section C) in both the 2008 and 2009 examinations when preparing assessment items. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 2 After interviewing the people in the Melbourne factory, Rose has produced a data flow diagram (DFD) of the a. State the names of the processes that are performed by the program MyCut DESIGNER.
1 mark - average 0.4 • produce engineering and cost data b. State which of the PCs are used to perform the 'Validate client data' and 'Create new job' processes. PC1 - the manager's. 1 mark - average 0.9
It would make sure all the required client data was present and reasonable (e.g. name exists, postcode is 4 digits) in order to get in touch with them again. 1 mark - average 0.3 A possible response could have been checking the data entry to ensure only reasonable data is allowed into the system. It was clear from students' responses that they had a general understanding of validation and why it is used, with many answering 'to check data' or 'to validate data'. However, very few students could articulate a clear definition of the process 'validate client data'. The study design defines validate as 'to check that data input to a computer system is of an appropriate type for processing and within acceptable boundaries' (page 52). Although this is the definition all students should study, responses clearly indicated that very few students had actively studied the glossary. Teachers are encouraged to copy the glossary for all students and test their understanding and knowledge of written definitions throughout the year. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proposed system Rose has found that the My Cut software is designed only to work on local area networks. To allow work to be shared between factories she proposes that a large format scanner be placed in each factory. The purpose of the scanner will be to scan house plans. Rose also proposes the following procedure, using the Melbourne factory as an example. Step 1: When the Melbourne factory receives a set of plans for a house it will scan them and save each sheet as a separate Graphic Interchange Format (GIF) file. On average each set of plans has four separate sheets. Step 2: If the factory in Melbourne cannot do the design work, but the factory in Perth can, then the Melbourne factory will send the GIF files to Perth via the Internet. Step 3: When the Perth factory has entered the plans into its MyCut DESIGNER, it will export the engineering data and cost data to a text file. The text file will be sent to the Melbourne factory. Step 4: The Melbourne factory will import the text file into its MyCut DATABASE. It will then produce the cutting data and proceed as usual. Rose wants the scanner connected to PC1. She expects each GIF file to be at least 40 Mb in size. She also expects that each factory will scan about 250 sets of plans in a year. Adding the scanner will mean that other changes will have to be made to the system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 3 Apart from speaking to people or contacting MyCut, suggest how Rose might have found out that the software can only operate on a local area network. She might have tried it and failed. (Trial and error is a time-honoured experimentation technique!) The technical manual might have mentioned the fact. 2 marks - average 0.6 I wondering what the examiners were fishing for here... This question tested students' knowledge of documentation types. Correct responses included, for example, reading thetechnical manual (simply writing 'check documentation' was not sufficient) and checking the company's website. It was also acceptable to respond with 'by testing the software'. However, it was clear from responses that students either did not understand the question, as responses had nothing to do with documentation, or they did not read the question correctly and responded with 'call MyCut' or 'speak to someone else that has used the software'. These responses were both incorrect as the question stated that speaking to people or contacting MyCut should not be considered. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 4 Perform a suitable calculation and use your result to explain why the existing Internet connection in each factory will no longer be appropriate. Calculation Each set of plans averages 4 x 40M = 160M per set. V90 analogue modems can download at a theoretical maximum speed of 56Kbps, but (and here's the big but) they can upload at a maximum speed of 33.6 Kbps! At 33.6 Kbps to upload 160MB, the dialup modem would take... 160,000,000 bytes * 8 bits = 1,280,000,000 bits / 33600 bps = 38,095 seconds = 635 minutes = 10.5 hours per set of plans! Most students probably said it would take about 8 hours, assuming upload speeds were 56Kbps (and that 56K was actually attainable in real life - which is hardly ever is. Never mind - the principle is still right. Explanation It would take an entire extra-long working day to transmit the files for a single set of plans! 3 marks - average 1.2 How many people remembered the asymmetric speeds of V90? I bet no kids knew it... Possible calculations included: Students could also multiply any of the above by four, as on average each set of plans involved four pages. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 5 The system software, office software and MyCut DATABASE on PCI currently take up about 16 gigabytes (Gb) of disk space. 4 sheets * 40MB * 250 times a year = 40,000MB = 40GB (roughly) of GIFs + 16GB of other stuff = 56GB total. 1 mark - average 0.3 Students did not need to show the calculation; it is shown here for explanation purposes only. Let's not get embroiled in a Gigabytes vs Gibibytes argument! Gibibytes sound like a breakfast cereal. b. In each factory many flammable materials are stored to keep the machinery working. Rose proposes that in the new system a full backup of PC1's files is made at the end of every day. Suggest a suitable backup medium. Justify your answer. Portable (USB or eSATA) hard disk drive. They are fast, capacious, reliable, very portable (easy to take offsite for storage), freely available to buy, and extremely cheap per megabyte of storage. In the past I would have said DAT tape, but the DAT drives are expensive, tapes are expensive and wear out, and HDD would surpass them in every measure nowadays. 2 marks - average 1.1
Following is an example of an acceptable student response. A suitable backup medium for PC1 is an external hard drive. As the amount of data on PC1 could be quite large, storage mediums such as CDs and DVDs will be ineffective as Truss-Tees will need a large number of them. An external hard drive will be suitable as they can be purchased in a large size (eg150GB) and will be able to store all the backup files from PC1 each day. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 6 PC1 will need to be upgraded in the new system. Rose has short-listed three computers whose specifications are shown in the table below. Taking into account Rose's plans for PC1, as stated in the proposed system, list the three most important specifications she needs to consider in order to choose the most appropriate computer. Explain why each of these specifications is important for the new PC1.
Specification 1 Storage Explanation It needs to store at least 56G, with room for expansion later. All of the hard disks above would qualify. Specification 2 CPU Explanation A fast CPU would increase the efficiency of processing large images and performing normal office tasks. Specification 3 RAM Explanation The more RAM (up to the limits the operating system can actually use) the more efficient the computer will process data and be able to multitask. 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 marks. State average was 3.4 RAM and CPU could easily be swapped. They are about equal in terms of importance. I didn't choose Connectivity because even an average NIC (100Mbps) is far faster than the fastest typical current internet speed (23Mbps). The screen size and number of USB ports is not really important to the case study. The designers would probably care for bigger screens, but not PC1. Possible answers included: The question was answered with varying degrees of success. Students were asked to list the three most important |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 7 During her analysis of the system, Rose interviewed all the assemblers in the Melbourne factory. One assembler mentioned that sometimes RoboCut would reject a good piece of timber. Function Check_Length(Timber_Length, LengthRequired) Begin
End Rose decides to test this algorithm by choosing a length of timber (Timber_Length) of 2.4 metres. For the other variable (Length_Required) she chooses the values 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5. a. Explain why Rose selected these values. They are boundary conditions to test the behaviour near, on, and beyond the critical point where the behaviour of the algorithm should change. Most subtle (and hard-to-find) errors tend to occur right at the point where behaviours should change, so test data should focus on that transition point. 3 marks - average 2.0 Following is an example of an acceptable student response. b. Complete the following table showing what the algorithm should return and what it actually returns.
2 marks - average 0.8 c. Explain why RoboCut only sometimes rejects a good piece of timber. It only accepts pieces longer than the length required, and rejects pieces are exactly equal to the length required. 1 mark - average 0.6 d. State one alteration to the algorithm that would correct this error. > should be changed to >= 1 mark - average 0.8 Hmm. A pretty basic > vs >= scenario. Not too imaginative. • If Timber_Length >= Length_Required Then |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 8 Rose recommended changes to the system's hardware and hoped to keep the software unchanged. However she now realises that there is a software fault that must also be corrected. MyCut is reluctant to believe that its software has a fault. Rose contacts some of her friends in the software industry and finds one who says he can provide her with the source code for the MyCut software. This will allow her to make her own changes to the program and correct the fault herself. Ethically, she should want to do everything she could to do what she was hired to do - fix the company's IT problem. This is even more understandable considering the difficult and obstructive attitude of the software company when Rose's request is reasonable. Legally speaking, using or modifying the software without permission would contravene the Copyright Act 1968. 4 marks - average 1.8 Be sure to name relevant laws accurately. Vague references to actions "being illegal" is not as convincing. For a number of years the examination has contained an ethical and/or legal-type question, and this year it continued to be answered poorly. However, many students were able to write an appropriate comment about copyright concerns. In the 2008 Assessment Report it was stated that students should 'contrast the two views and add further relevant information showing their understanding.' However, many students again did not provide this type of response. This is an area that students need to focus on during their examination preparation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Question 9 (2011-2014 - the qualities of suppliers is not relevant any more) The new system requires a significant hardware purchase by Truss-Tee of a large format scanner for each of its factories. Two suppliers have been identified that can provide scanners with the right technical specifications for Truss-Tee at a comparable price of about $ 13,000 each. To help Truss-Tee choose between the two suppliers, identify two other factors that are important for Truss-Tee to consider and explain why these factors are important for Truss-Tee. Possibilities include:
4 marks - average 1.9 I did include hardware/technical compatibility issues at first, but as Adrian Janson pointed out, the question did say that the scanners had the right technical specs for Truss-Tee. There were many possible answers to this question, including (but not limited to): This question posed similar problems to Question 6, with students appearing to misunderstand what the question was |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Question 10 (2011-2014 - skip this. Implementation methods are no longer relevant) Rose believes that Truss-Tee should use a pilot changeover method to the new system. She suggests to Shaun that the Melbourne factory should be the first to change. Shaun realises that for the new system that Rose has proposed, a pilot changeover will not work. a. Identify the feature of the new system that makes a pilot changeover inappropriate. The unconverted branches' old hardware would not be compatible with the pilot branch (particularly relating to transmission speeds). Also, the other branches would not be able to send plans to Melbourne because they don't have scanners. 1 mark - average 0.3 Appropriate responses included: b. Explain why this feature makes a pilot changeover inappropriate. Other branches would not be able to receive plans with the Melbourne branch within a working day. Other branches would not be able to send plans to Melbourne because they don't have scanners. 1 mark - average 0.4 Other factories will not able to receive/handle GIF files in a timely manner, therefore the new system will not function as required. c. Recommend and justify a changeover method that Truss-Tee could use. For them to work as a team, all branches would need to convert directly and simultaneously to the new system. It could not be phased in within a branch because all parts of the new system are required for it to work. 2 marks - average 0.7 Direct changeover – all factories will then be able to send/receive GIF files so the new system can be fully functional, unlike the pilot if only one factory has high speed Internet access. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Question 11 Now that Truss-Tee has upgraded its computer network it needs to improve its network security to ensure the protection of its information. For each type of protection solution listed below, provide an example and explain how it provides protection for Truss-Tee's information. Software solution - network login and password (or biometric ID) > stops unauthorised people accessing workstations - firewall > protects the LANs against unauthorised external access. - virus/malware scanner > guards against viruses, worms, trojans, adware, spyware that could damage or steal data or information or misuse their system to send spam or DDOS attacks. - encryption > to make their files unreadable to unauthorised people, and to protect it during transmission (e.g. PGP) - backups > to recover data after it has been damaged or lost Physical solution - lock branch doors, bar their windows > prevent access by thieves or vandals - fire alarms, extinguishers > detect & fight fires - swipe cards > to control who uses which doors and when - UPS for the server > protect it from power surges, brownouts and blackouts - put the server in an airconditioned room > protect the server against damaging heat and humidity - make the server room locked with a restricted key > prevent unauthorised access to the vulnerable server, even by unauthorised employees - burglar sensors & alarms, surveillance cameras > detects breakins - lock workstations down to desks > physically deter attempts to pick up and steal equipment and their data (1 +2) + (l +2) = 6 marks - average 3.3 Again, students found it difficult to construct clear and detailed responses. Many students were able to give examples of security such as virus checkers, a firewall, username/password (software solutions) and access protection, such as swipe card, biometric, surveillance measures, alarms, guards, etc. (physical), but many struggled to provided an explanation about how it would provide protection for the Truss-Tee information. Students need to practise writing responses that fully answer a question. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Question 12 Truss-Tee is establishing the evaluation criteria for the new system. The main system goal is to efficiently and effectively share the design workload between all the sites. In order to measure the success of this it has determined a number of criteria that must be met. Criterion 1 Criterion 2 The table below outlines the evaluation strategy Truss-Tee has put in place to measure one of these criteria. Complete the table to outline a strategy they could use to evaluate the second criterion.
5 marks - average 1.8
On the other hand, I found this question just plain dull and tedious!
This question required students to complete the table for Criterion 2, with Criterion 1 provided as an example of what was expected. Even though Criterion 1 was modelled for students, most students were not able to complete this question. It was clear that most students found the evaluation stage of the System Development Life Cycle a challenge to understand and articulate. Many students did not provide a response to the question. Students should be encouraged to write a response for every question. This is another area that teachers should concentrate on as part of examination preparation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total 49 marks END OF QUESTION AND ANSWER BOOK |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
On the whole, a good paper. Unusually for SD, it got one Dog's Breakfast award and a couple of slaps on the tail for being bad. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Back to the IT Lecture Notes index
Back to the last page you visited
Created 18 November 2009
Last changed: March 9, 2022 11:34 AM
Original Content © Mark Kelly 2008
Images and questions are © Victorian Curriculum
and Assessment Authority 2009. Reproduced here with permission for educational purposes.
VCE Applied Computing Notes © Mark Kelly